交流电路功率分析
瞬时功率
Instantaneous Power
The instantaneous power (in watts) is the power at any instant of time.
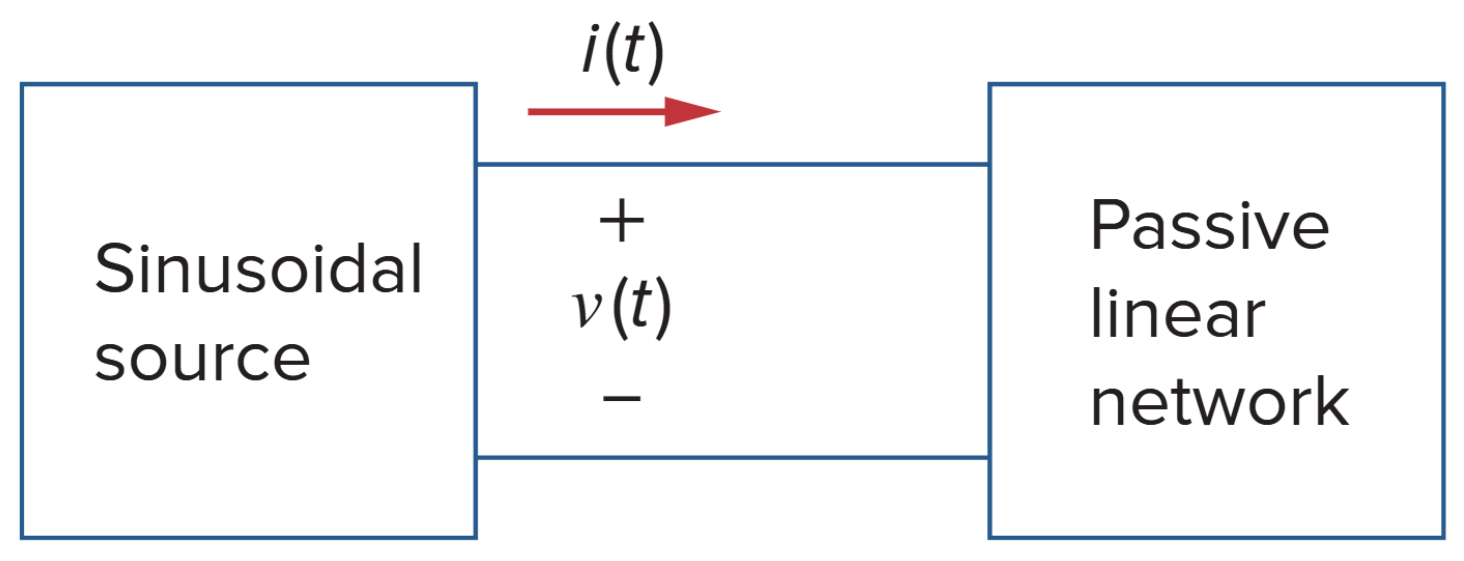
如图,假设电路的电压和电流可以表示为正弦量
则瞬时功率可以表示为
应用三角函数积化和差公式
得到
可以看到,瞬时功率的计算公式非常复杂,难以直接计算。
平均功率
Average Power
The average power, in watts, is the average of the instantaneous power over one period.
对瞬时功率公式进行一个周期的积分
上式为平均功率的时域表达式。为了获取其相量域表达式,注意到
总结,交流电路平均功率表达式为
最大平均功率传输
Maximum Average Power Transfer
For maximum average power transfer, the load impedence ZL must be equal to the complex conjugate of the Thevenin impedance ZTh.
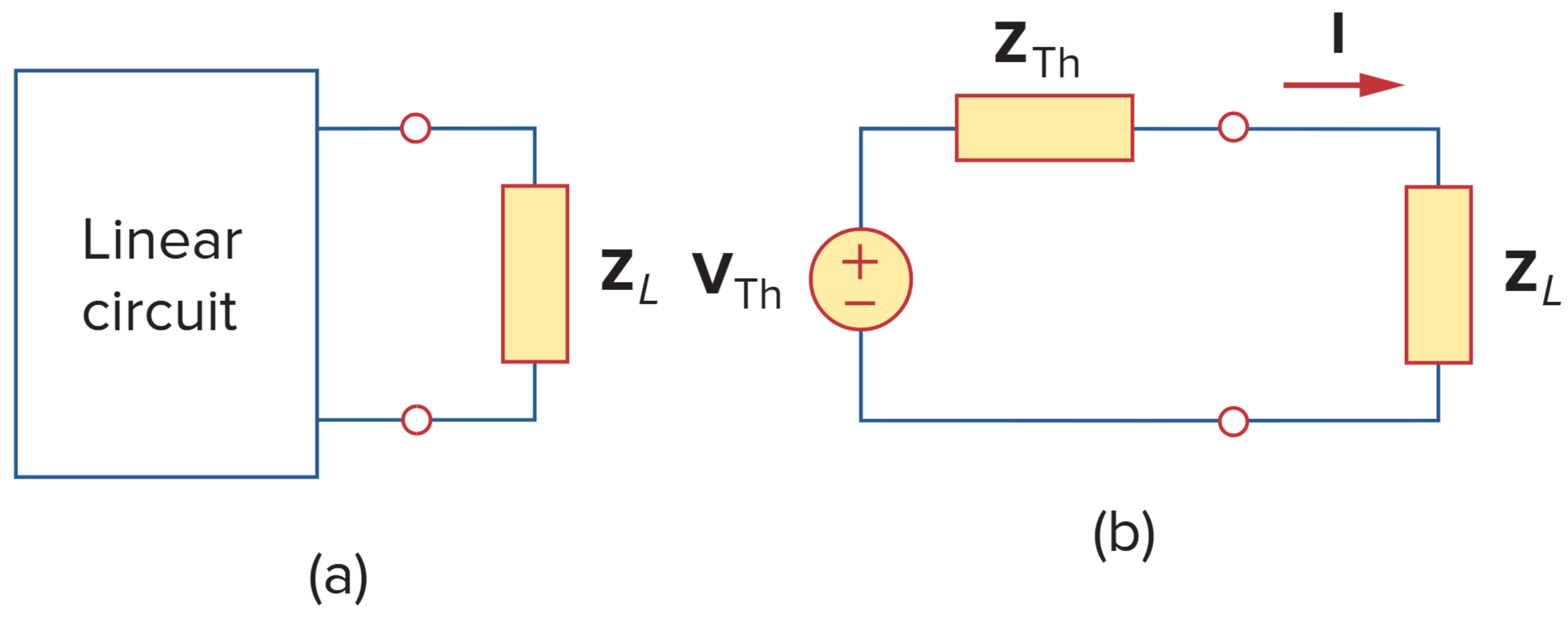
如图,假设 VTh 和 ZTh 为电路的戴维南等效电压、阻抗值,ZL 为负载阻抗。并且
流经负载的电流为
传递到负载的平均功率为
其中,注意
以及
为了使负载获得最大平均功率,能够调整的参数只有负载的 RL 和 XL,所以需要求 P 关于 RL 和 XL 的偏导数,并令其等于零
先回顾一下乘积求导公式和除法求导公式
求 P 关于 RL 和 XL 的偏导数,并令其等于零
结合上述两个偏微分方程的结果,为了实现最大平均功率传输,负载阻抗 ZL 必须使得 XL = -XTh,并且 RL = RTh。
于是,最大平均功率为
有效值或均方根值
Effective or RMS Value
The effective value of a periodic current is the dc current that delivers the same average power to a resistor as the periodic current.
The effective value of a periodic signal is its root mean square (rms) value.
常用公式
视在功率和功率因数
Apparent Power and Power Factor
The apparent power (in VA) is the product of the rms values of voltage and current.
The power factor is the cosine of the phase difference between voltage and current. It is also the cosine of the angle of the load impedance.
复功率
Complex Power
Complex power (in VA) is the product of the rms voltage phasor and the complex conjugate of the rms current phasor. As a complex quantity, its real part is real power P and its imaginary part is reactive power Q.
- Complex Power
- Apparent Power
- Real Power
- Reactive Power
- Power Factor
The complex, real, and reactive powers of the sources equal the respective sums of the complex, real, and reactive powers of the individual loads.
功率因数校正
Power Factor Correction
The process of increasing the power factor without altering the voltage or current to the original load is known as power factor correction.
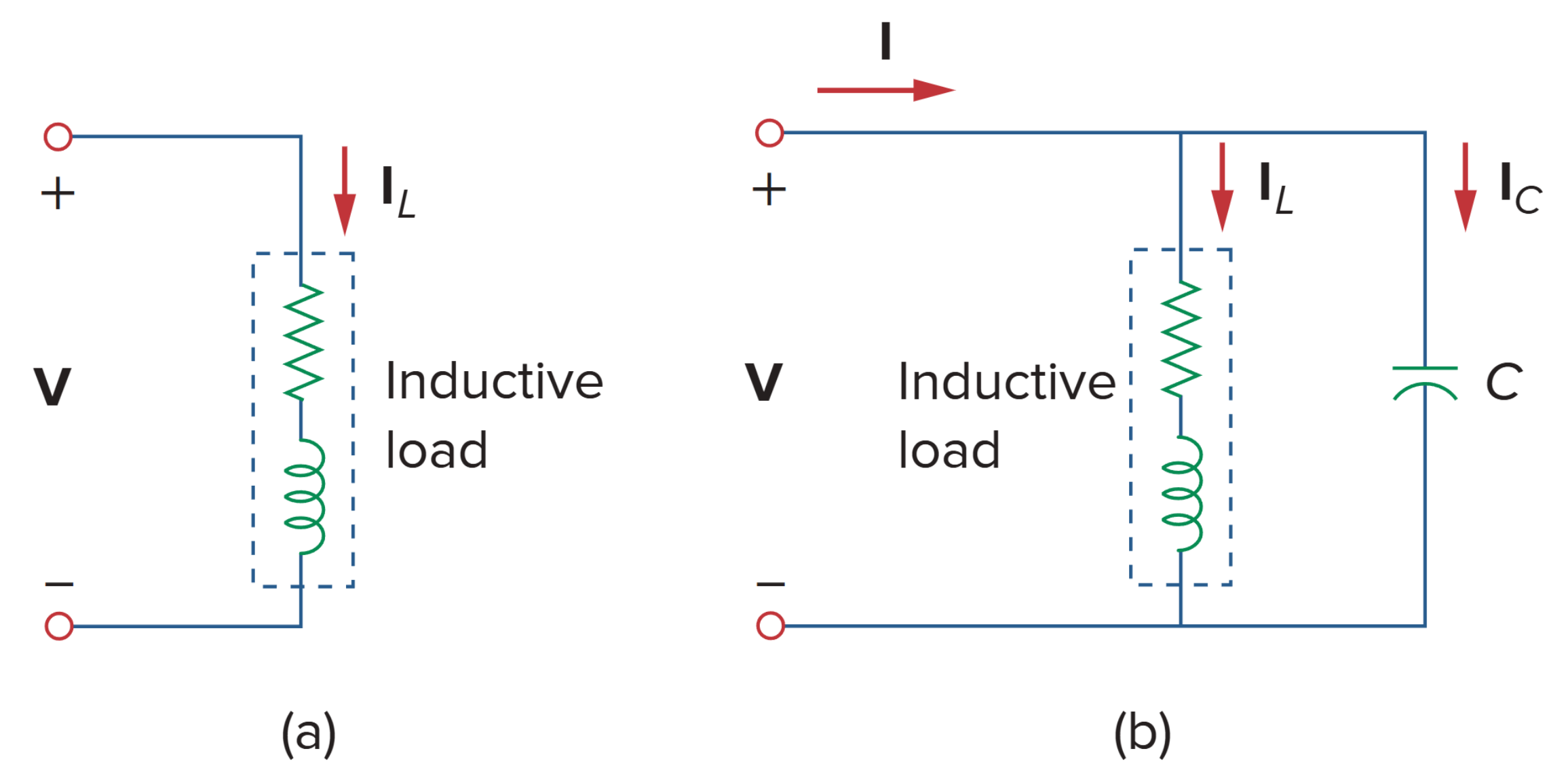
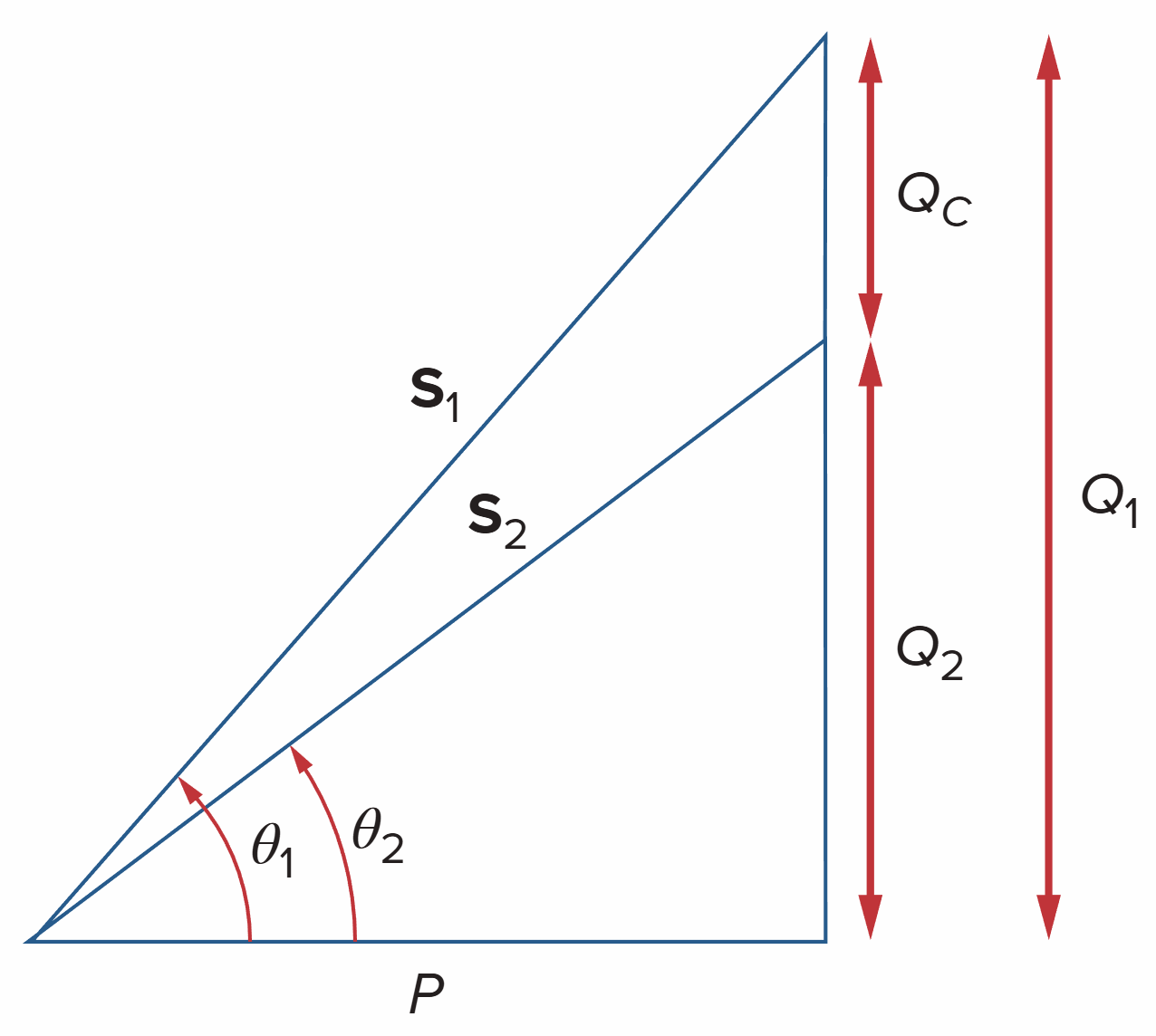
以下分析需要满足电容并联在原感性负载两端,以确保 real power P 不变。
