电路理论
线性电路
A linear circuit is one whose output is, linearly related (or directly proportional) to its input.
叠加原理
The superposition principle states that the voltage across (or current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone.
源变换
A source transformation is the process of replacing a voltage source vs in series with a resistor R by a current source is in parallel with a resistor R, or vice versa.
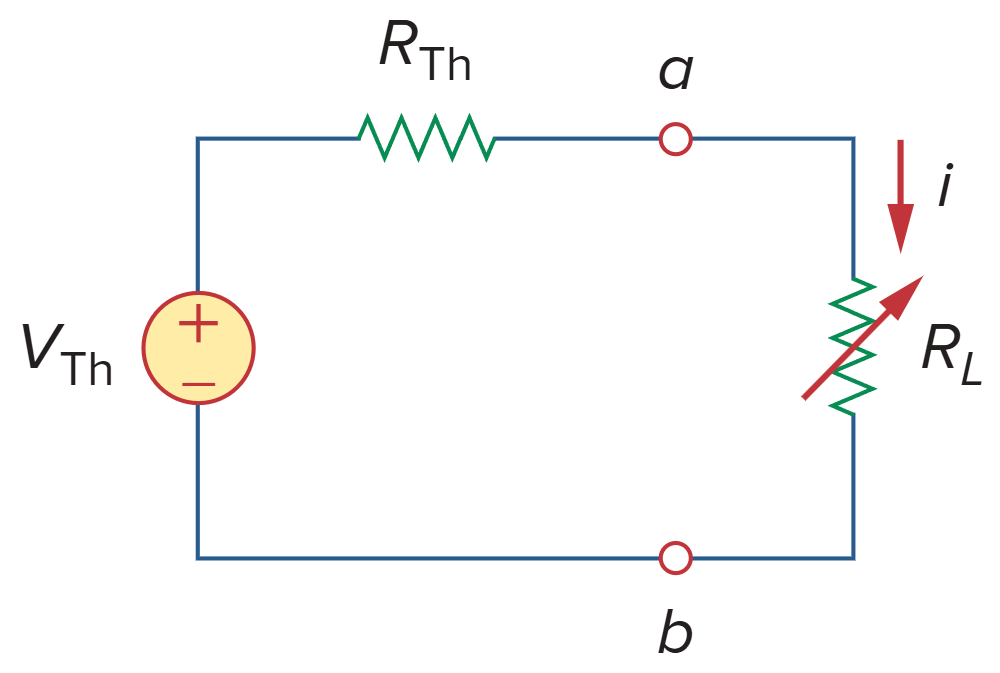
戴维南定理
Thevenin's theorem states that a linear two-terminal circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a voltage source Vth in series with a resistor Rth, where Vth is the open-circuit voltage at the terminals and Rth is the input or equivalent resistance at the terminals when the independent sources are turned off.
诺顿定理
Norton's theorem states that a linear two-terminal circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source IN in parallel with a resistor RN, where IN is the short-circuit current through the terminals and RN is the input or equivalent resistance at the terminals when the independent sources are turned off.
最大功率传输
Maximum power is transferred to the load when the load resistance equals the Thevenin resistance as seen from the load (RL = RTh).