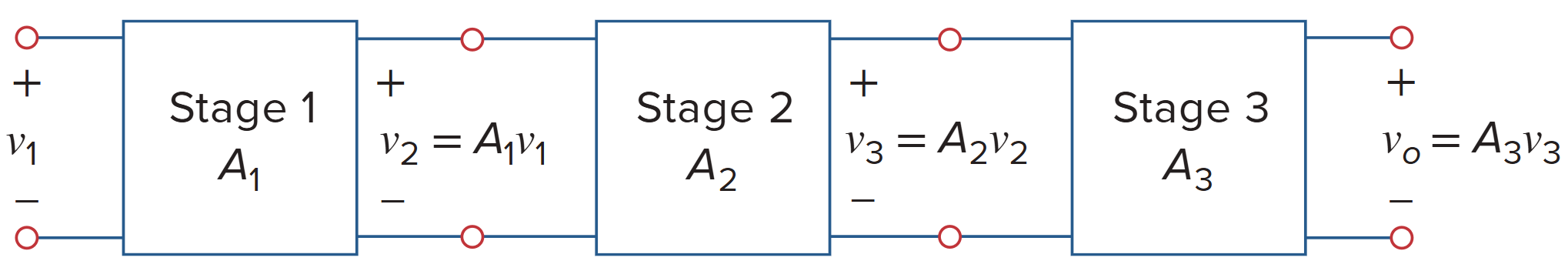运算放大器
Operational Amplifiers
The op amp is an electronic unit that behaves like a voltage-controlled voltage source.
An op amp is an active circuit element designed to perform mathematical operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, differentiation, and integration.
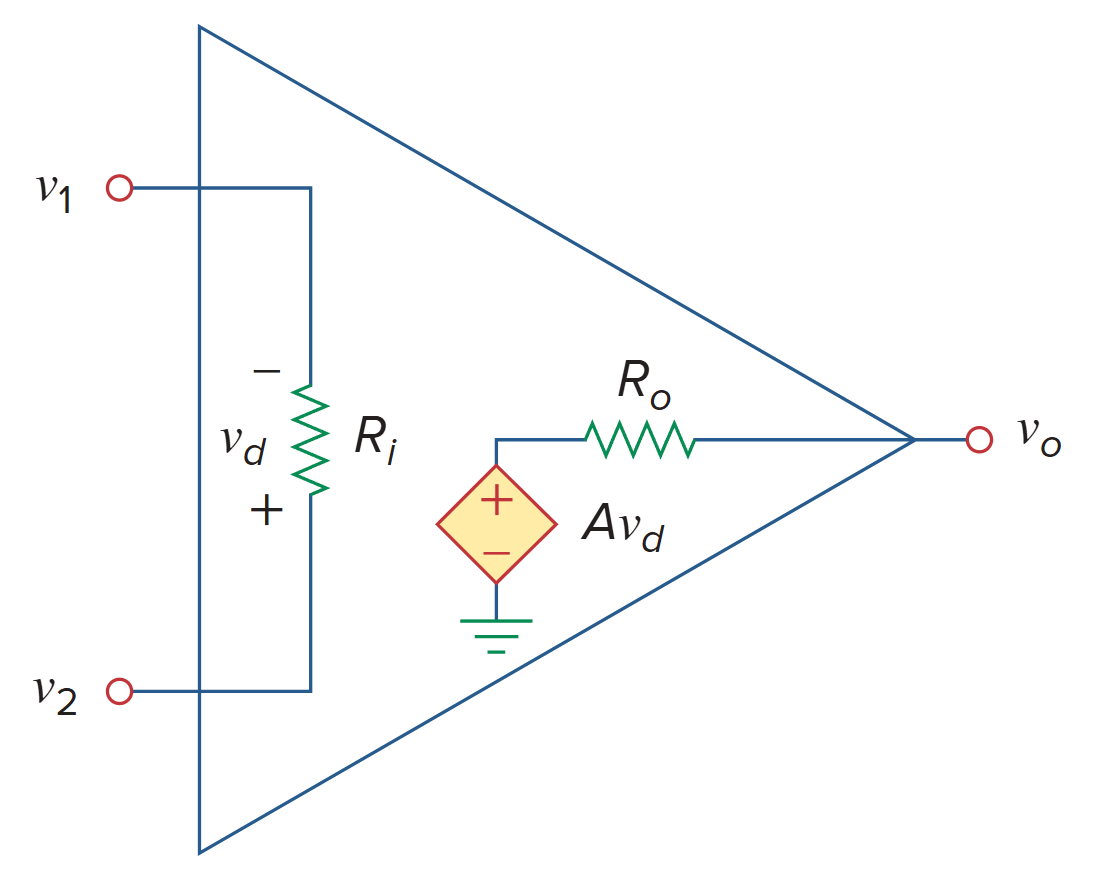
理想运算放大器
Ider Op Amp
An ideal op amp is an amplifier with infinite open-loop gain, infinite input resistance, and zero output resistance.
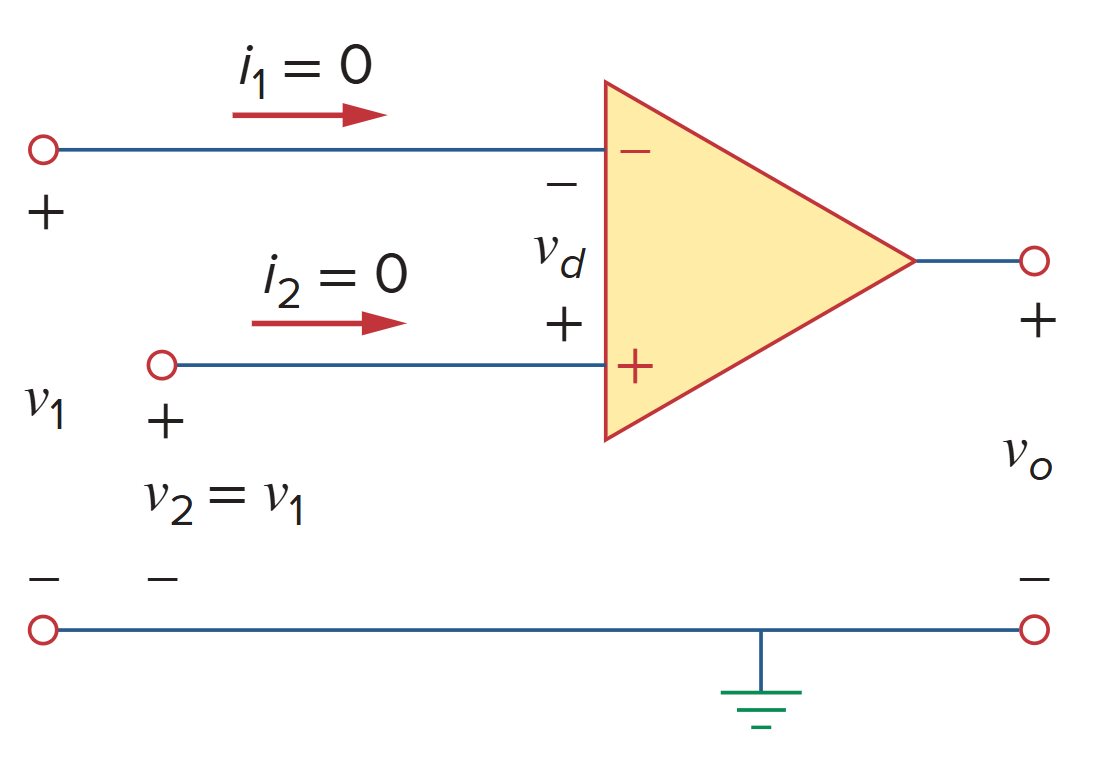
- The currents into both input terminals are zero:
- The voltage across the input terminals is equal to zero:
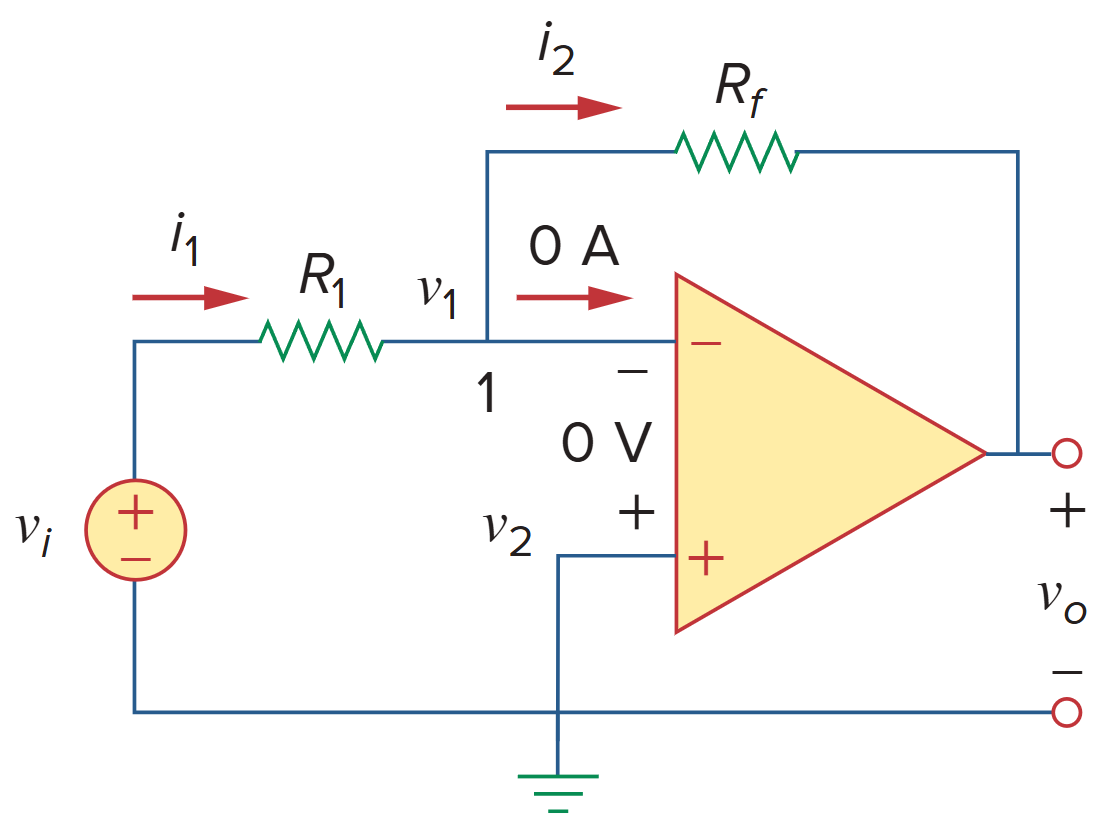
反相放大器
Inverting Amplifier
An inverting amplifier reverses the polarity of the input signal while amplifying it.
同相放大器
Noninverting Amplifier
A noninverting amplifier amplifies is an op amp circuit designed to provide a positive voltage gain.
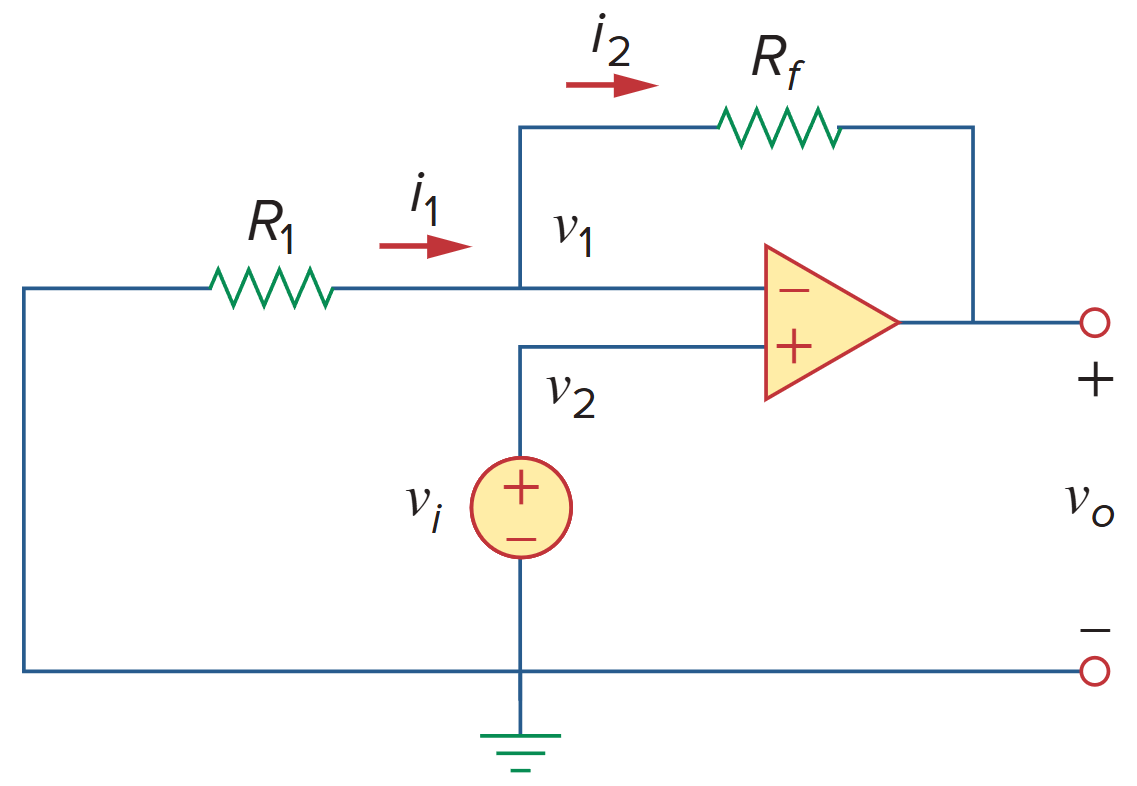
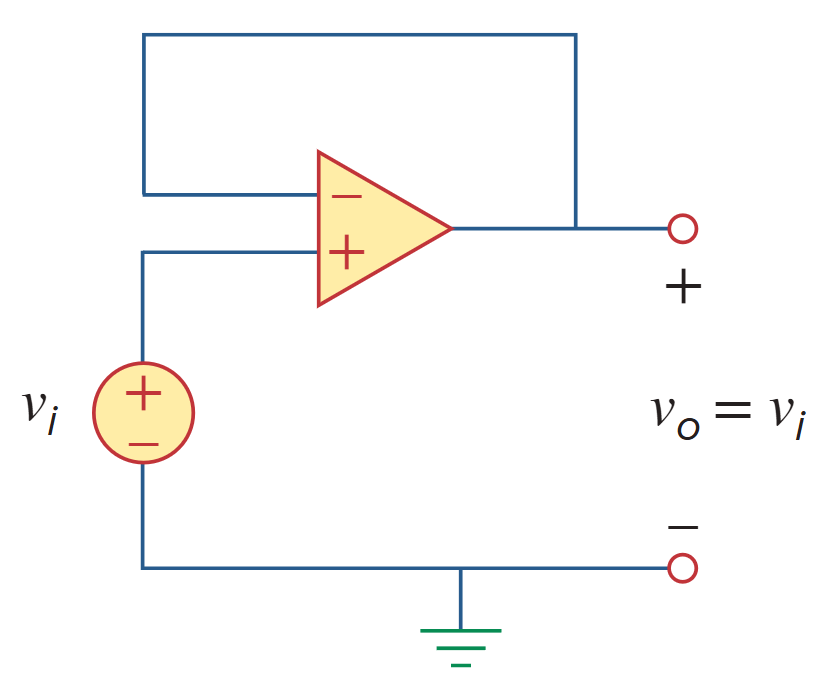
电压跟随器
Voltage Follower.
When Rf = 0 (short circuit) or R1 = ∞ (open circuit) or both, the gain becomes 1. Under these conditions (Rf = 0 and R1 = ∞), the circuit in figure above becomes that shown in figure below, which is called a voltage follower (or unity gain amplifier) because the output follows the input. Thus, for a voltage follower
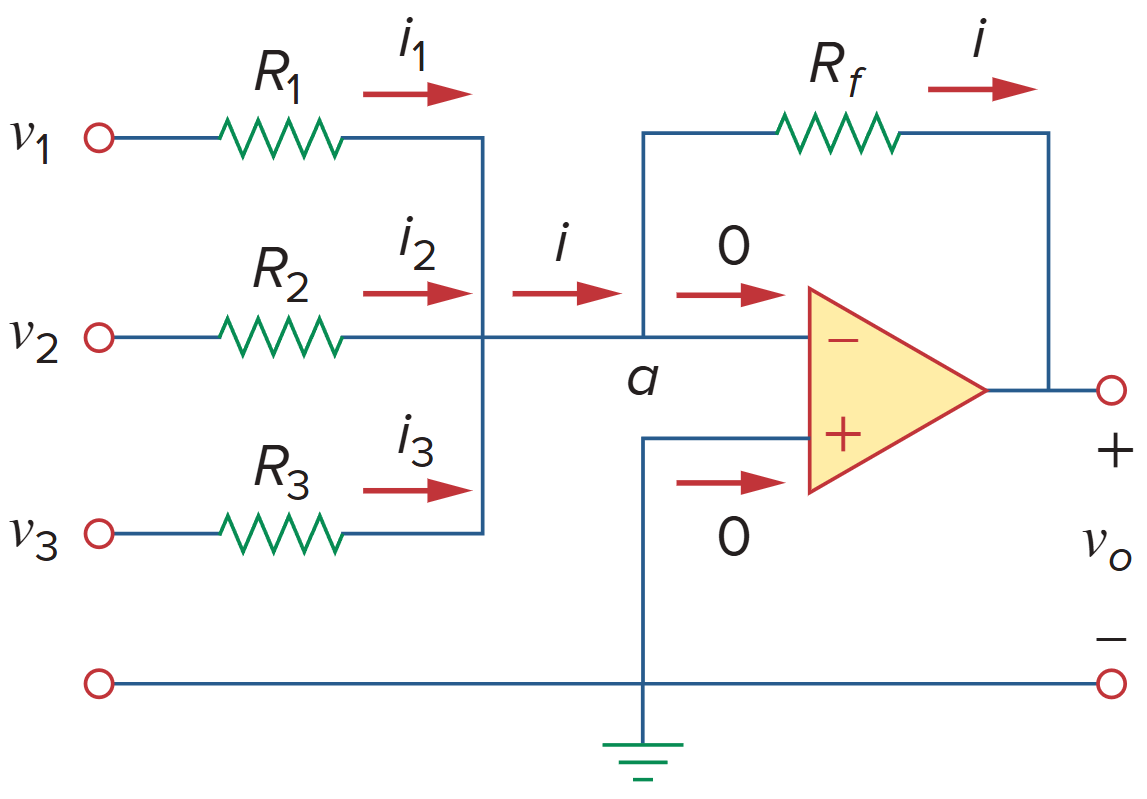
求和放大器
Summing Amplifier
A summing amplifier is an op amp circuit that combines several inputs and produces an output that is the weighted sum of the inputs.
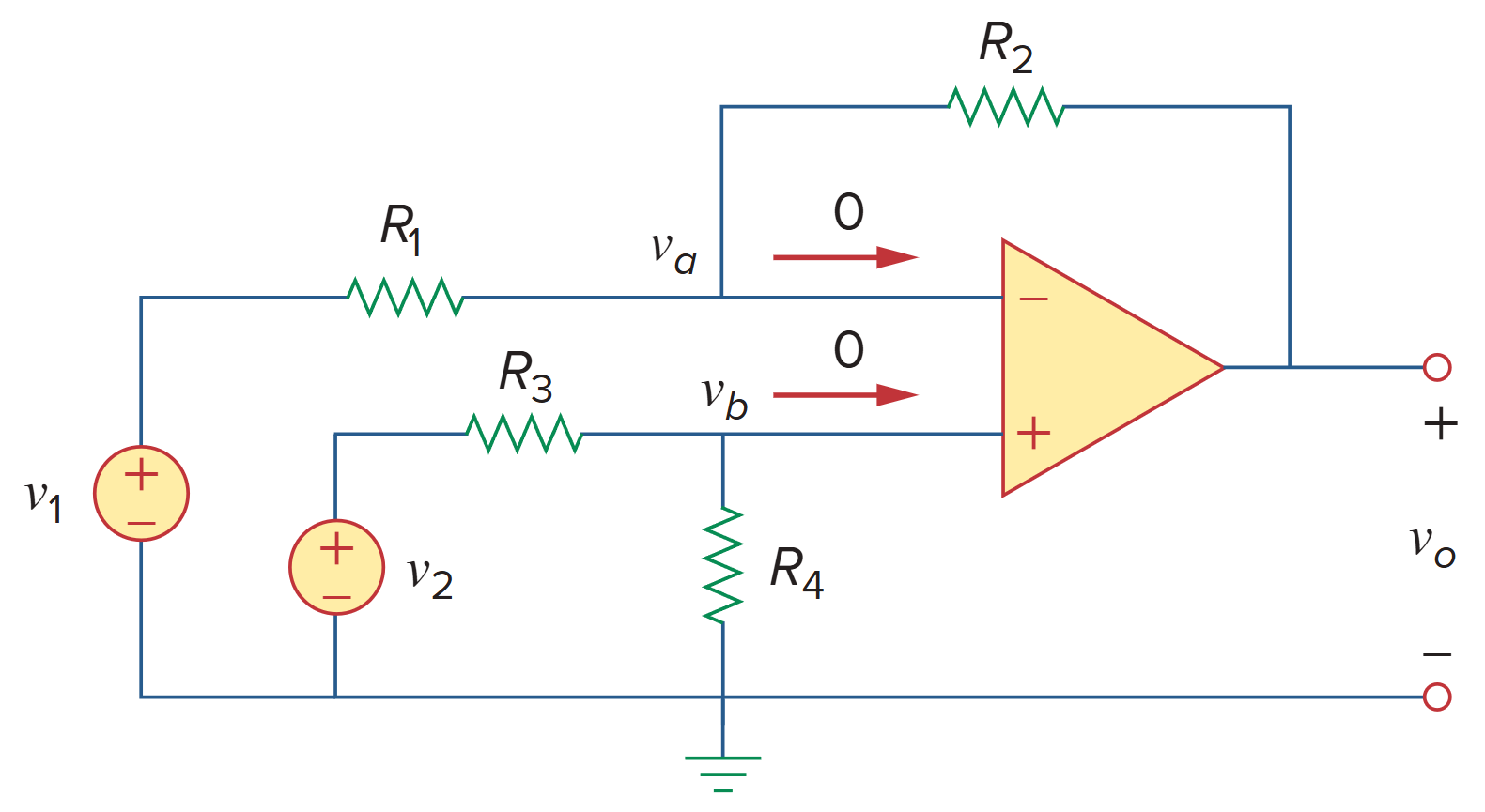
差分放大器
Differential Amplifier
A differential amplifier is a device that amplifies the difference between two input but rejects any signals common to the two inputs.
级联运算放大器
Cascaded Op Amp Circuits
A cascaded op amp circuit is a head-to-tail arrangement of two or more op amp circuits such that the output of one is the input of the next.